CyberKids: An AI-integrated Cybersecurity Awareness Game using Roblox Platform
This project showcases my end-to-end development of an interactive cybersecurity learning platform built using Roblox Studio, Spring Boot, and modern web technologies. CyberKids combines game-based learning with real-time classroom management by implementing multi-level gameplay, RESTful API integrations, encrypted student registration, and a teacher analytics dashboard. Throughout the project, I applied principles from usability engineering, systems design, and full-stack development to create an engaging, educational experience optimized for elementary learners and classroom workflows.
Project Screenshots
• Teacher Dashboard
Built using React 18, Tailwind CSS, and Shadcn
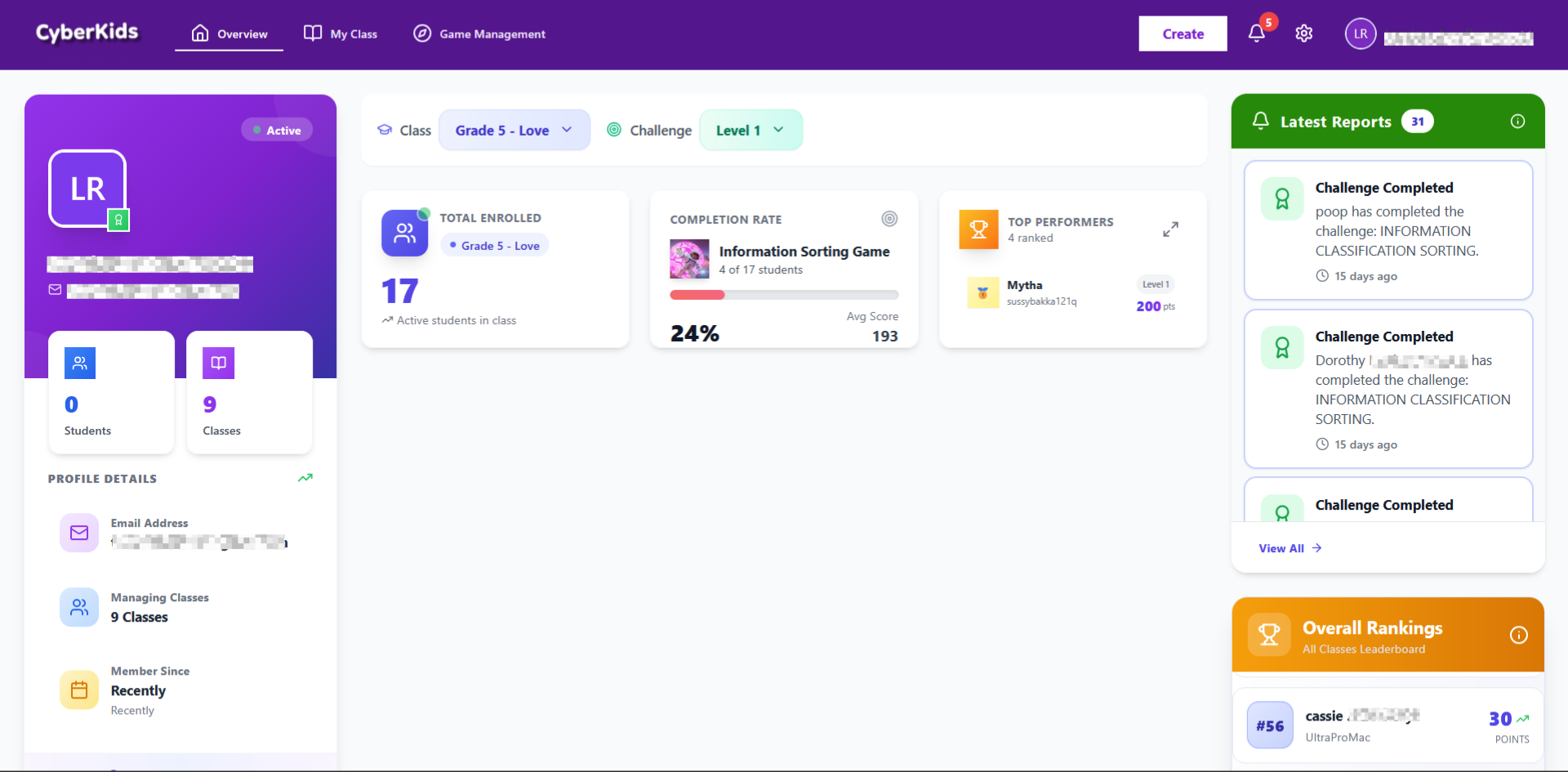
Dashboard Overview
• Student Experience
Built using Spring Boot and Roblox Studio
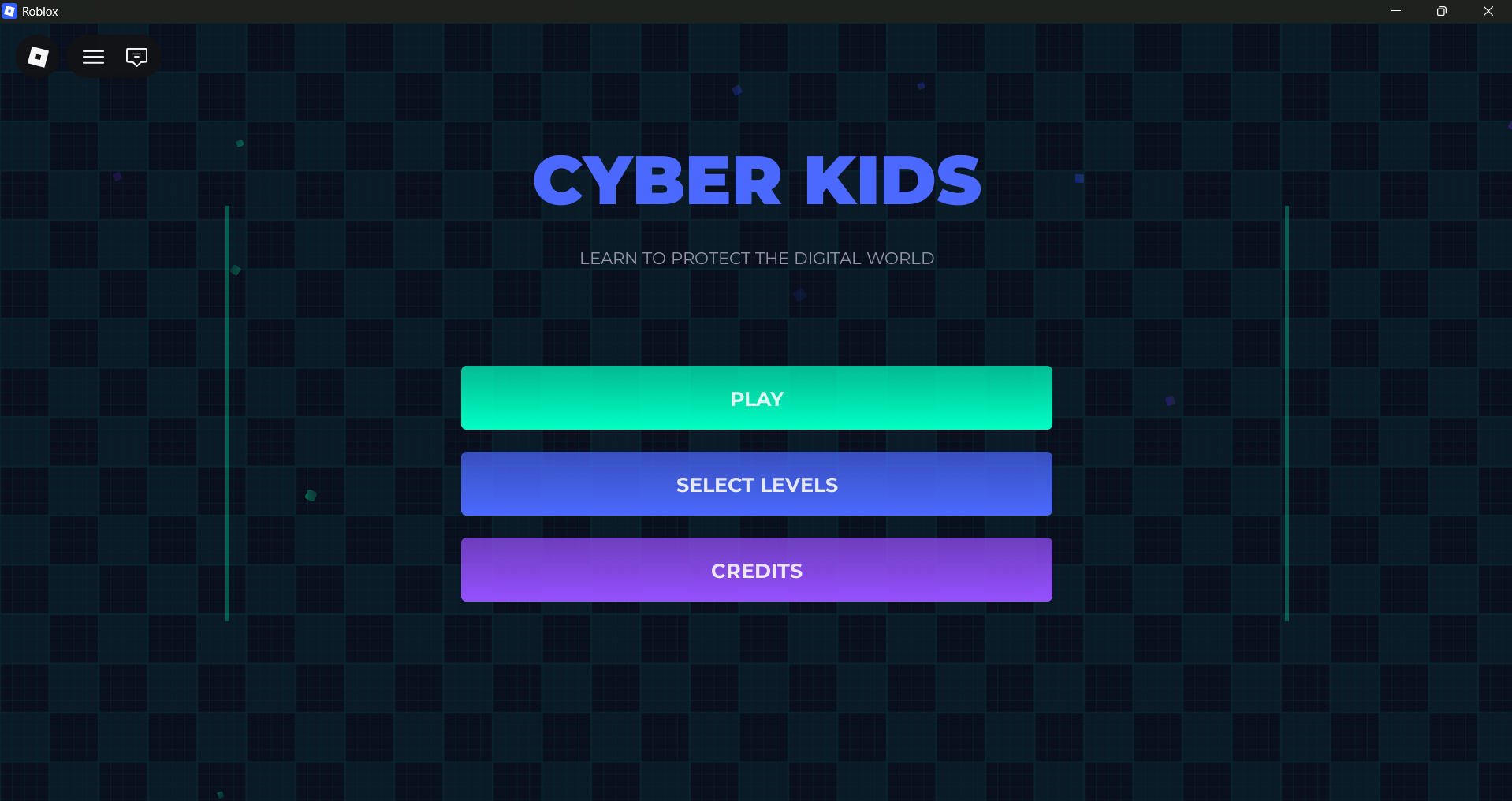
Main Menu
Key Features
- • Multi-Level Roblox Gameplay: Three interactive levels that teach online privacy, password security, and phishing awareness through hands-on challenges.
- • Real-Time Teacher Dashboard: Web app for monitoring student progress, viewing analytics, and managing class settings.
- • Secure Student Registration: Identity-linked registration system with encrypted name storage and backend validation.
- • REST-Powered Game Integration: Roblox gameplay communicates with the backend through custom RESTful API endpoints for scoring, timers, and level tracking.
- • AI-Driven Learning Feedback: Context-aware feedback that explains answers, reinforces lessons, and improves understanding.
- • Real-Time Notifications: Live teacher alerts for student logins, level completions, and progress milestones.
- • Designed for Classroom Usability: Developed with UPA-based testing to ensure learnability, engagement, and ease of use for Grades 5–6 students.
Technology Stack
 Spring Boot
Spring Boot React
React Tailwind CSS
Tailwind CSS Roblox Studio
Roblox Studio MySQL
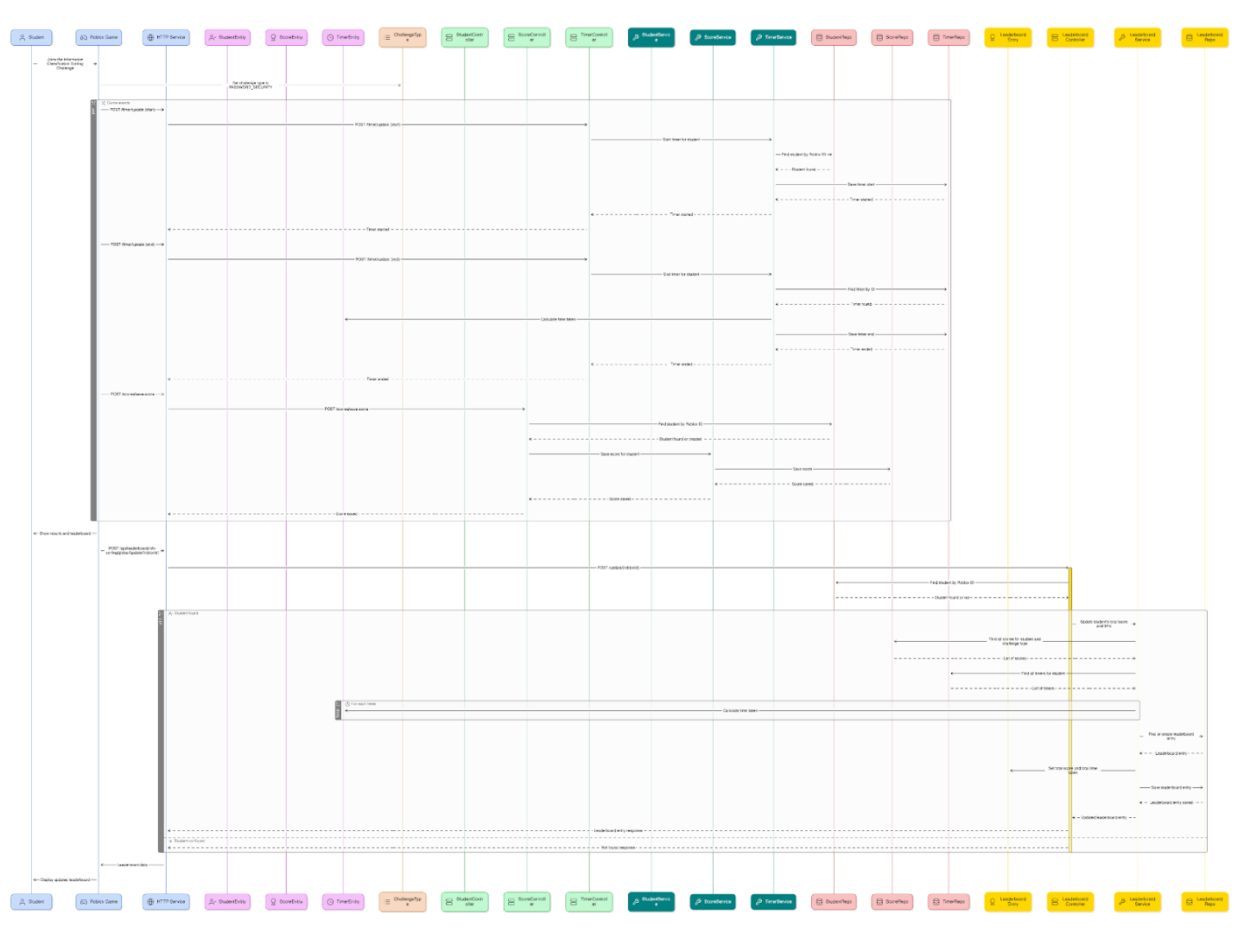
MySQLSystem Architecture Overview
CyberKids was built with a modular and low-cost architecture to support scalable development under real student constraints. This architecture allows parallel development, faster debugging, and agile iteration. This design keeps the system lightweight and easy to update independently.
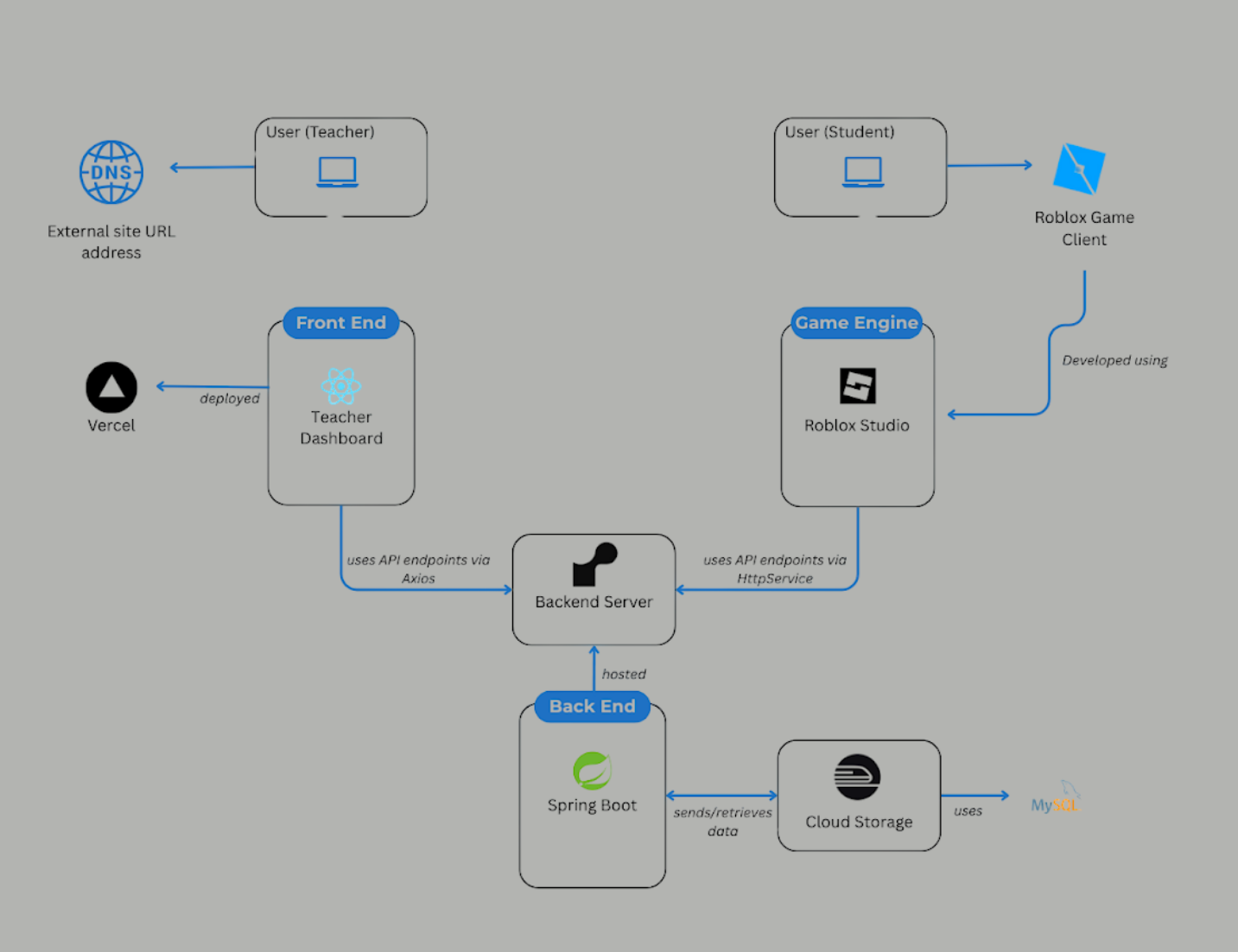
Back-End Architecture
Technical Implementation
The backend was designed to handle registration, scoring, timing, and leaderboard operations between the Roblox game client and the system’s database. The core architecture consists of the following components:
- Entities: Define the database structures for Students, Timers, Scores, Teachers, Scenarios, and Leaderboard entries, storing all persistent gameplay and configuration data.
- Repositories (Repo): Use Spring Data JPA to provide CRUD operations for each entity, acting as the primary data access layer for student, timing, score, scenario, and leaderboard records.
- DTOs: Handle structured input and output between the backend and the Roblox client or teacher dashboard, ensuring clean data transfer without exposing internal entity models.
- Services: Contain the business logic for student management, scoring, timing, scenario validation, and leaderboard computation while keeping controllers lightweight and modular.
- Controllers: Provide REST API endpoints for Roblox and teacher interactions—such as registering students, submitting scores, retrieving scenarios, and fetching leaderboard data.
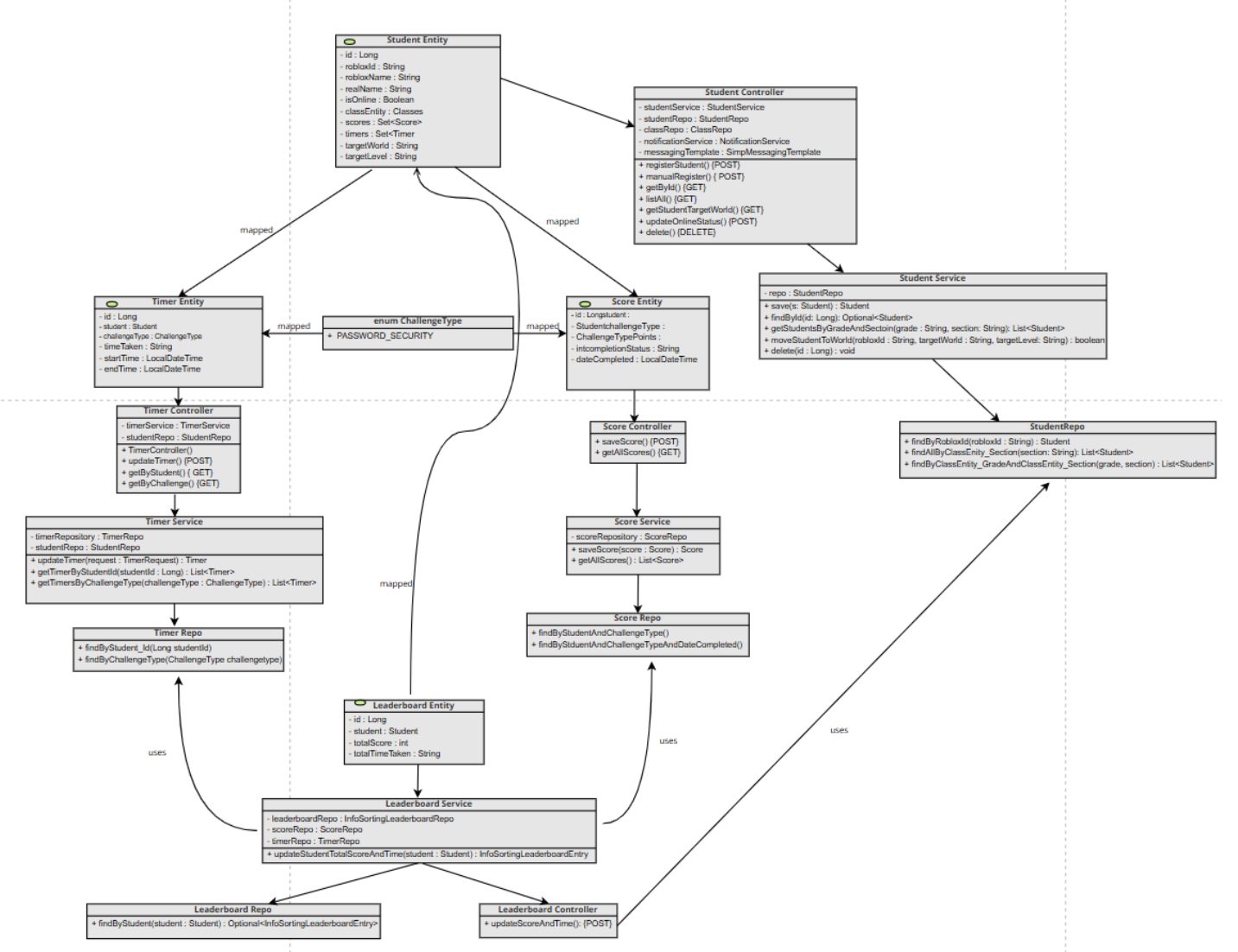
Data Flow
Sequence Diagram
The data flow illustrates how requests from the Roblox game client travel through the backend and how responses are generated. A sequence diagram best represents this process by showing the step-by-step interactions between Controllers, Services, Repositories, and the Database.
- Client Request: The Roblox game sends an HTTP request (e.g., register student, submit score, start timer) to the appropriate backend API endpoint.
- Controller Processing: The Controller receives the request, validates input using DTOs, and forwards it to the corresponding Service for business logic execution.
- Service Logic Execution: The Service performs core operations such as creating records, updating status, computing scores, or retrieving scenarios. It communicates with the Repository layer as needed.
- Repository & Database Access: The Repository executes database operations (CRUD) on Entities. Data is read from or written to the persistent storage through JPA.
- Response to Client: After processing, the Service returns the result to the Controller, which then sends a structured JSON response back to the Roblox client or teacher dashboard.